
Advanced cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) – Advanced cardiovascular life support (ACLS)
This chapter discusses interventions and evaluations performed during advanced cardiovascular
The clinician's base
The Cardiovascular Medicine section is a comprehensive resource that encompasses all aspects of cardiovascular disease. This section is meticulously curated to provide clinicians with in-depth knowledge across a spectrum of cardiovascular topics. All chapters are continuously updated and new chapters added.

This chapter discusses interventions and evaluations performed during advanced cardiovascular
Cardiac arrest is a result of tachyarrhythmia, bradyarrhythmia or asystole.
Basic life support (BLS) can be provided by anyone, including
This page summarises the most current recommendations for the management
It is commonly stated that approximately 80% of all cardiac
Predicting sudden cardiac arrest The purpose of discovering and measuring

The forces that drive coronary and cerebral perfusion, and ventilation

Eletrical alternans: an ECG sign of pericardial effusion and cardiac
The course from sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) to death follows
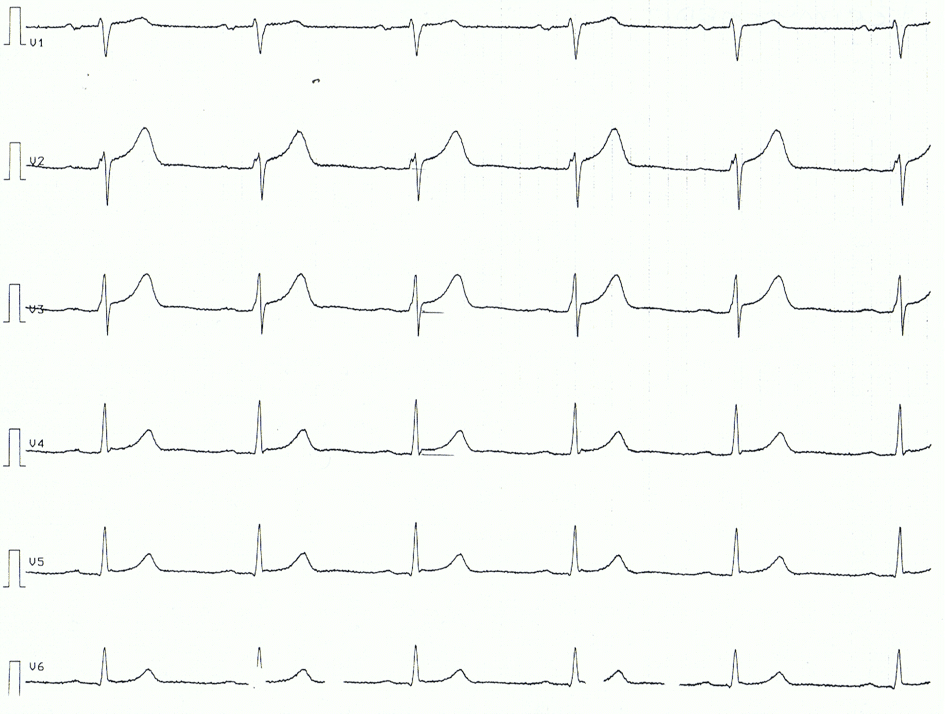
Pericarditis, myocarditis and perimyocarditis: ECG changes and clinical features The

Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (broken heart syndrome, apical ballooning syndrome, stress induced
Time is the most critical factor for survival in cardiac

The early repolarization pattern and syndrome: from ECG criteria to management
Data sources for monitoring cardiac arrest and resuscitation There are

Brugada syndrome: A life-threatening arrhythmia with unknown prevalence Pedro Brugada
Hearts too good to die In 1961 the Journal of

J-wave syndromes: early repolarization pattern, Brugada syndrome, hypercalcemia and hypothermia
SCA (Sudden Cardiac Arrest): Sudden and unexpected cardiac arrest with
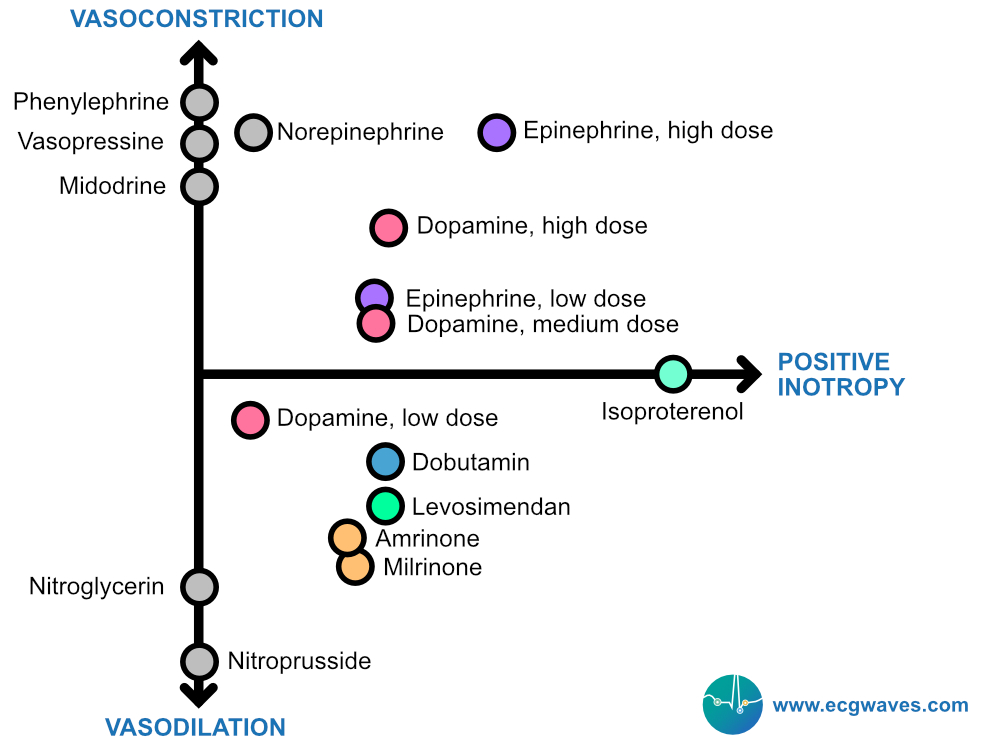
Inotropes and vasopressors Vasopressors induce vasoconstriction and increase mean arterial
Heart rate (bpm) = 60000 / cycle length Cycle length

Antiarrhythmic drugs and management of ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation This
This drug manual is provided for use in patients with
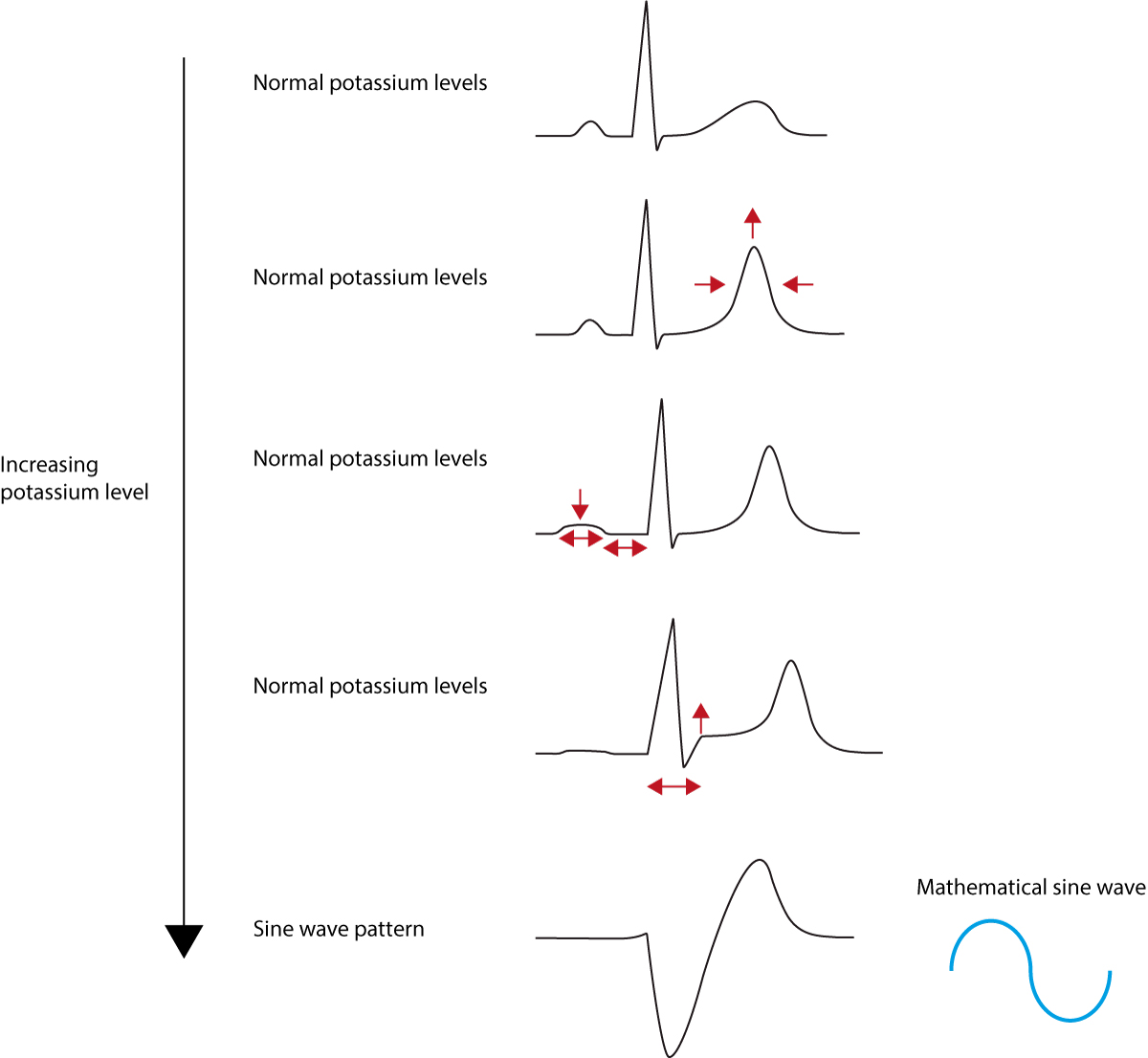
ECG changes due to electrolyte imbalance (electrolyte disorder) The normal cardiac action
The effect of antiarrhythmic drugs, beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers
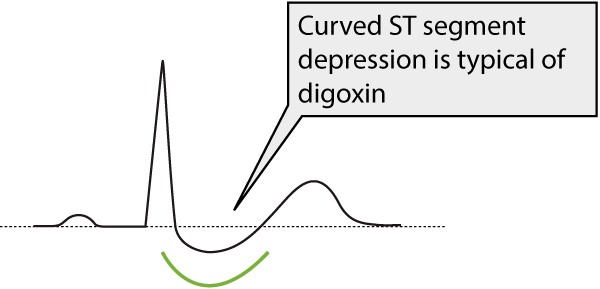
Digoxin ECG changes: arrhythmias, conduction defects and waveform changes Digoxin
Pericardial diseases: effusion and tamponade A long series of conditions
Constrictive pericarditis: the end stage of pericardial inflammation Constrictive pericarditis
Cardiac tumors Cardiac tumors are rare. They can occur anywhere
Right ventricular strain When assessing the right half of the
Endocarditis Endocarditis implies that a bacterial infection engages the heart

Cardiac thromboembolism Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death worldwide
The best ECG book is not the one making it

Echocardiography in Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) and Grown Up Congenital

Aortic regurgitation Aortic regurgitation implies that the aortic valve leaks

Mitral regurgitation Causes of mitral regurgitation The most common cause
Pulmonary (pulmonic) regurgitation Pulmonary regurgitation is also called pulmonic regurgitation. The
Pulmonary (pulmonic) stenosis Pulmonary stenosis is virtually always a consequence

Tricuspid regurgitation The tricuspid valve separates the right ventricle and
We are dedicated to empowering clinicians with the most current, in-depth knowledge in cardiovascular medicine. Our platform offers a unique blend of expert insights, e-books, revision resources, and practical tools, designed to enhance your clinical practice and patient care. Join our community of dedicated healthcare professionals and elevate your practice evidence-based cardiovascular medicine.

From cell to reperfusion
The Cardiovascular 2026
